Introduction
Mora Jai boxes are simple-looking puzzles that can be configured into a huge variety of challenges. The original set of puzzles from Blue Prince mostly have short, simple solutions (2-20 moves), but lengthy and difficult solutions can be constructed by exploring deeper state spaces of the tile grid.
Initially, I wanted to create a list of the most difficult configurations by cataloging the longest solutions, but it turns out that length is not the best predictor of difficulty. Many of the longest solutions rely on repetitive patterns rather than complex logic and novel mechanics.
Ultimately, the list of Challenge puzzles in my simulator was found using a combination of brute-force search, automated filtering, and manual inspection.
Definitions
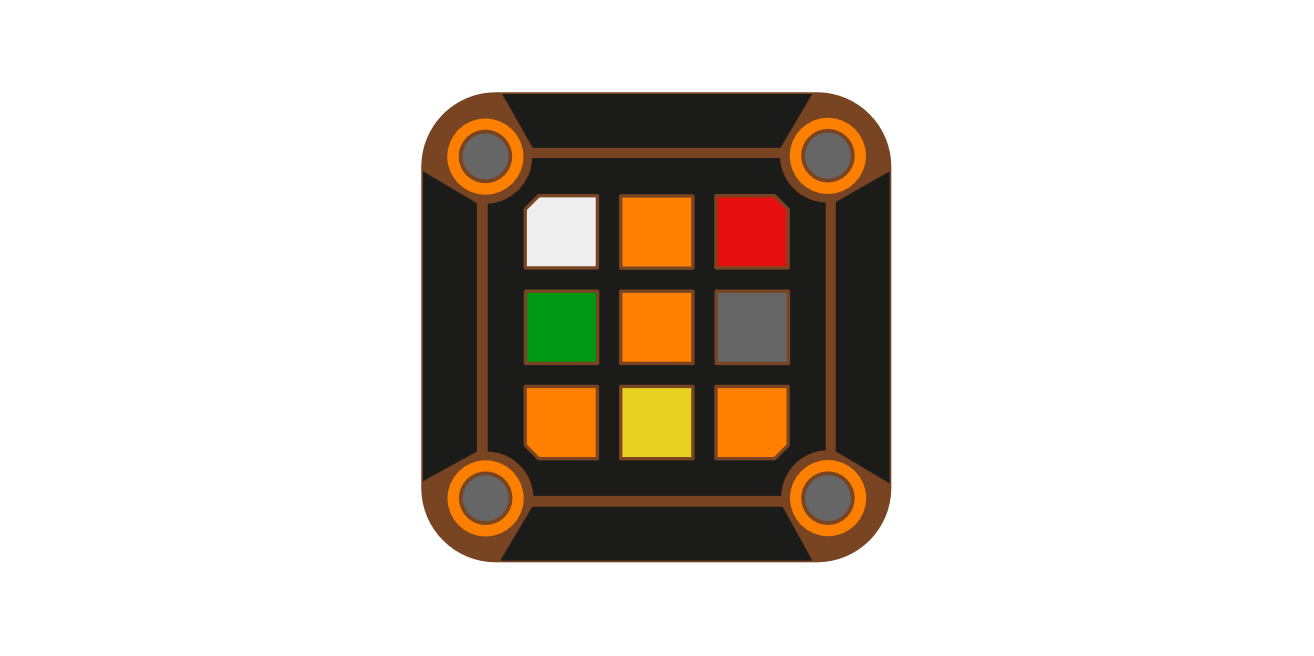
- Colors - [Expand]
- Tile - One of 9 inner colored tiles
- Outer Button - One of 4 round colored buttons
- State - The color configuration of the outer buttons and tiles
- Depth - The minimum number of moves required to solve a given state
- Solvable State - An initial configuration that can be solved using the correct sequence of tile presses
- Solved State - A state where the colors of the 4 corner tiles match their corresponding outer buttons
- Box - A Mora Jai puzzle with a specific outer button configuration
- Symmetry - A transformation that can be applied to a box to produce a box with an equivalent solution
Solution Space
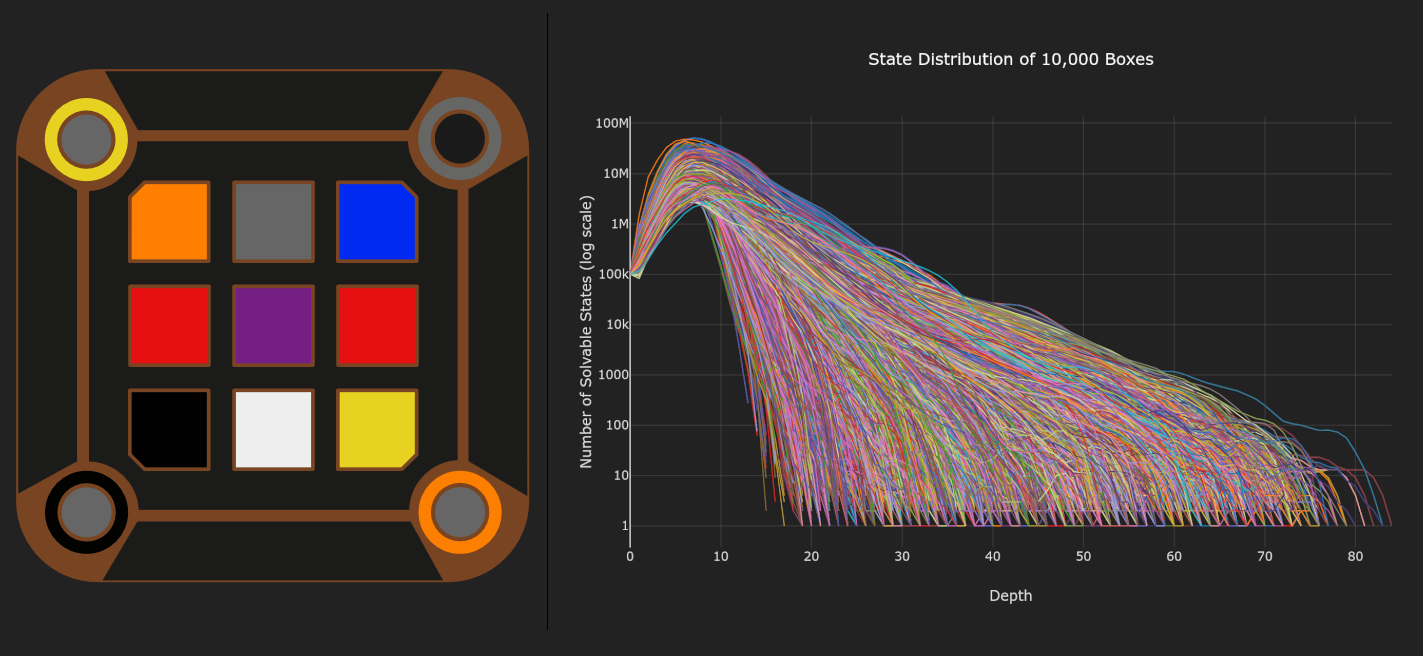
The Mora Jai Box solution space is large, but still analyzable using optimized brute-force algorithms.
There are 10,000 (10⁴) possible outer button configurations (“boxes”), and each of these has a unique solution space.
For each outer button configuration, there are 1 billion (10⁹) possible ways to set the inner tiles.
The inner tile presses could be mapped out completely for efficient searching using a directed graph, but this graph would take up a huge chunk of memory that exceeded any RAM that I had available. Instead, I opted for an iterative approach on one box at a time, where each solved state is marked as depth “0”, then any state that can produce depth 0 is marked as depth 1, and so on. The state tracking array only requires 1GB of RAM. Without optimizations, the algorithm needs to iterate N times over 1 billion states, where N is the depth of the longest solution.
Unsolvable States
Many inner tile configurations cannot possibly lead to a solution. For instance, if one of the outer buttons is pink, but there are no pink tiles present in the puzzle, then the puzzle cannot be solved with any combination of tile presses. To speed up the analysis, we can filter out these unsolvable states.
In puzzles whose outer buttons consist of “simpler” colors (pink, green, yellow, violet), the state space can be initially reduced by over 90%. For the most complicated arrangements, the benefits shrink to 25%–50%.
Symmetries
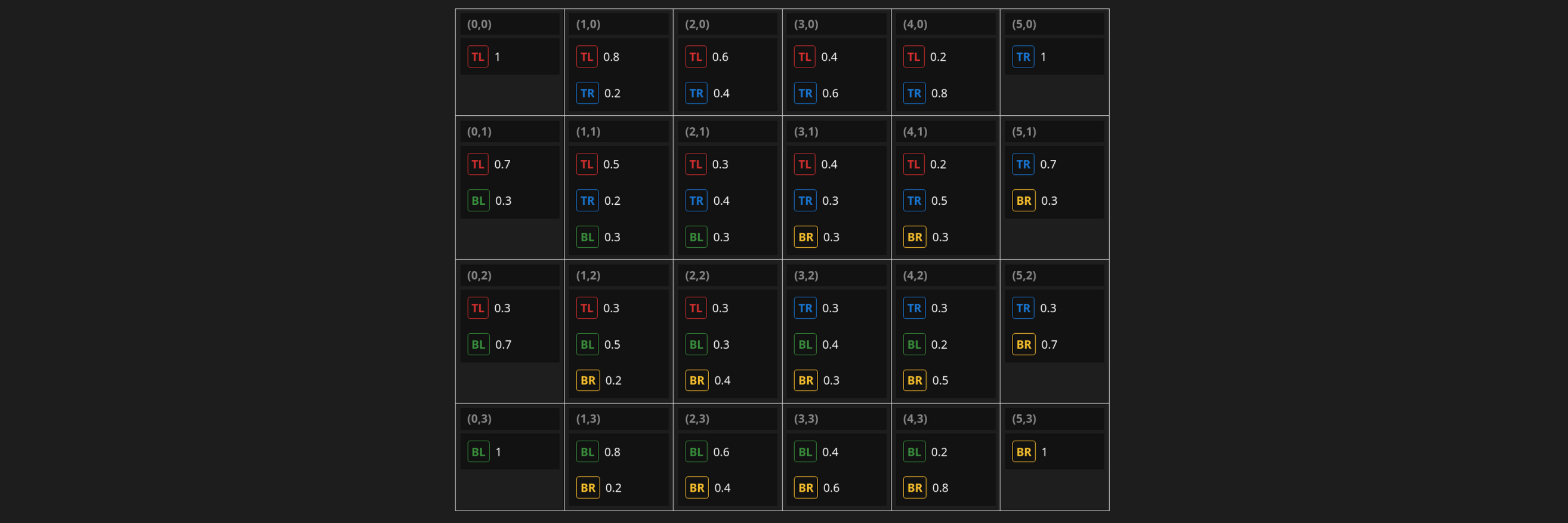
One might expect large overlaps in the solution space due to some key symmetries in the tile behaviors:
- Vertical symmetry: Black shifts its row right.
- 180° symmetry: Pink rotates surrounding tiles clockwise.
- Vertical or 180° symmetry: Violet (south movement) mirrors yellow (north movement).
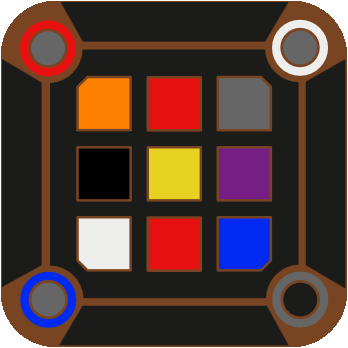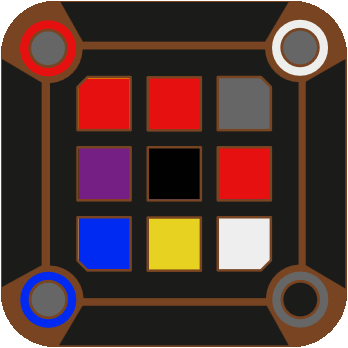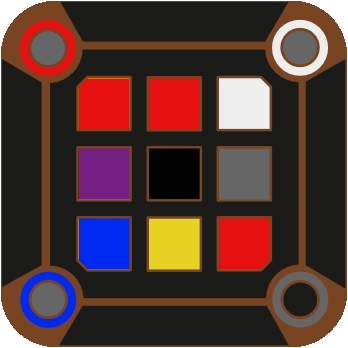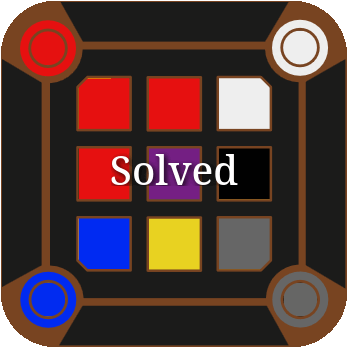
For example, these two configurations at depth 57 exhibit vertical symmetry with each other.
For a majority of cases, exchanging yellow with violet and vertically mirroring the outer button configuration produces nearly identical outcomes in the distribution graph. This plot shows the solution depths for the box with four yellow outer buttons, versus the box with four violet outer buttons:
The yellow and violet boxes both have a total of 64,492,718 solvable states, but looking closely (zoom in on depth 7-12), the state distribution is skewed slightly in the first half of the graph. Symmetry is broken whenever black and pink tiles co-exist in the same puzzle, and the varying solution lengths affect the shape of the graph. Deeper states tend to lack pink tiles, so the yellow & violet graphs converge after depth 30.
I did not make any assumptions about symmetry in my analysis due to the clear divergence that occurs at certain depths.
Implementation Details
The final depth analysis algorithm executes in three stages:
- Pruning (CPU): Using quick logical deduction, unsolvable (“dead”) states are eliminated from a box’s state space.
- Iteration (GPU or CPU): One depth at a time, beginning with the solved 0 state, the remaining states are submitted to an OpenCL kernel that simulates the puzzle’s button presses over every remaining state and marks the next depth. The GPU code is at least 10× faster than the CPU code.
- Backtracking (CPU): States that are part of a deeper state’s solution path are marked to be ignored in the detailed output. This step isn’t perfect since it doesn’t consider longer solution paths, but it increases the quality of data and makes manual review easier.
Multiple instances of the algorithm run in parallel, pulling work from a randomized queue of boxes to help distribute the CPU and GPU loads.
The source is available at https://github.com/cjgriscom/MoraJaiAnalysis.
Results
The program took 3 days to compute the state distribution for every box. It also cataloged the tile configurations for any depth with fewer than 2,000 states for manual inspection.
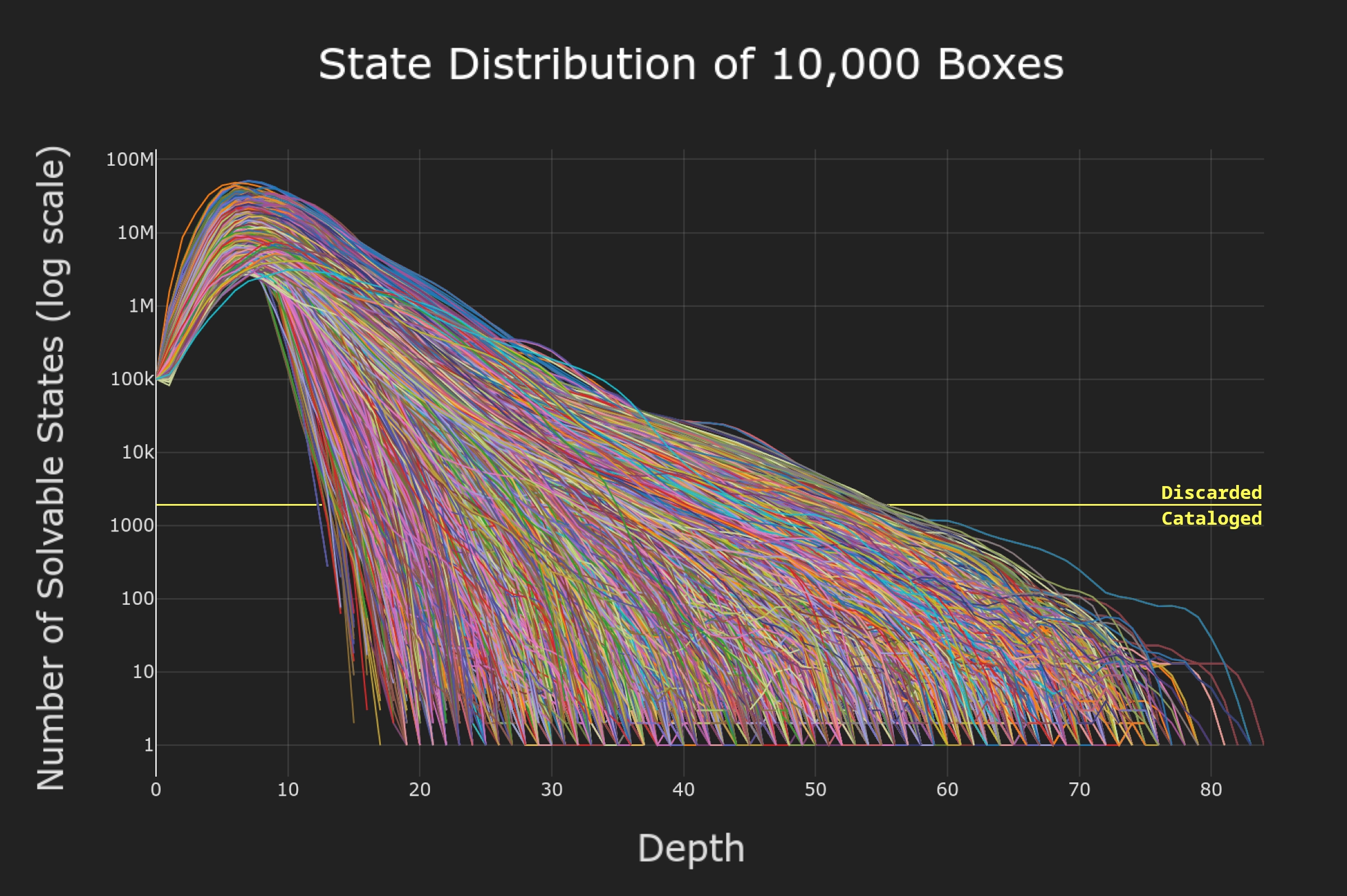
State Counts
Roughly ~10.45% of Mora Jai configurations are solvable. Below is the high level distribution breakdown, considering all 10,000 boxes.
| Unsolvable states | 8,955,265,607,521 |
| Solvable states (excluding depth 0) | 1,044,634,392,479 |
| Depth 0 states (already solved) | 100,000,000 |
| Total | 10,000,000,000,000 |
Depth Extrema
Below is the isolated data for the most extreme outer button configurations.
| Lowest solution depth | 13 | |
| Highest solution depth | 84 | |
| Fewest solvable states | 20,266,135 | |
| Most solvable states | 383,935,071 |
The longest optimal solution found was 84 moves. That configuration includes a gray target, which I allowed in the analysis despite their absence from Blue Prince. The longest optimal solution excluding boxes with gray targets is 79 moves.
Solution Tropes
Several common mechanics appear frequently in the deepest solutions. Color combinations that shuffle pieces in long, non-destructive loops tend to make up the bulk of many solution sequences. I included at least one example of each “trope” in the Challenge puzzle list, but in general I filtered them out to prioritize more unique solutions. Below are descriptions of the two most common tropes I encountered:
Trope 1: Center Column Function Selector
This mechanic features a center column whose tiles remain isolated within the column, but control the behavior of an outer blue tile. The tiles in the center column act as a selector that determines which operation the outer blue tile performs. This results in a repetitive sequence that gradually advances toward a solution.
Green, Yellow, Blue
Green, Green, Violet
The 67-move Challenge - Gray puzzle is the only included example of this mechanic. It also appears in the longest 4x red and 4x white boxes (omitted from the challenge list), and many other configurations in the 66-76 move range.
Trope 2: Center Row Shuffler
This mechanic requires yellow, violet, and black tiles positioned in the center row, along with a blue tile on the top or bottom row. The blue tile periodically drops in and out of the center row to reposition other pieces through a complex series of exchanges.
This mechanic usually appears alongside others, preceding or following key destructive moves, rather than completely dominating a solution sequence. It is present in Challenge - Black, Challenge - Violet, Challenge - Blue, and Challenge - Longest.
Conclusion
The final challenge list is intended as a representitive selection of the most difficult and distinctive Mora Jai Box configurations. While my manual analysis covered a substantial portion of the state space, it was not exhaustive, and many interesting configurations likely remain to be found. I welcome suggestions for additional puzzles to include, as well as feedback on the existing challenge list and analysis tools.
Appendix - Scratchpad
Use this tool to load a custom puzzle, count your moves, or automatically generate a solution.