Barycentric interpolation is an alternative way to generate a biaxial blend grid, suitable when the four corner formulations vary along just two independent values (for example, in pottery glazes: % silica on the X axis and % alumina on the Y axis). In most grid dimensions, this approach can reduce the number of source mixtures needed per cell to two or three, saving both material and measurement time.
Traditionally, biaxial grids are calculated using bilinear interpolation. This method works for any combination of four corner formulations and is more forgiving of inaccuracies in those corners, but it requires blending all four source mixtures for each interior cell.

Introduction
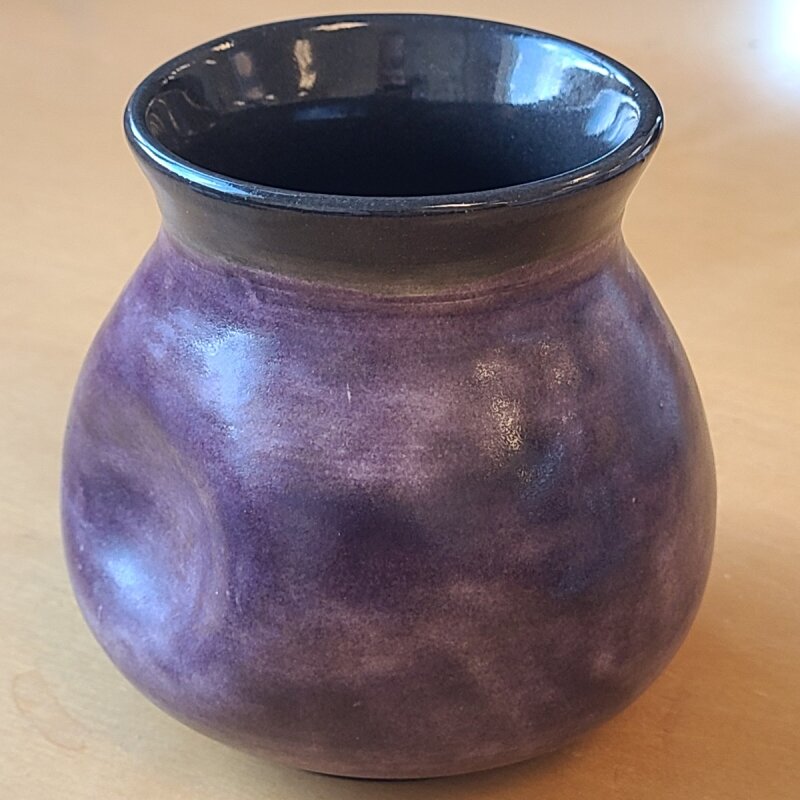
This page documents efforts to lower the firing temperature of David Tsabar’s high-fire Nickel Aubergine.
Purple is a tricky color in pottery that can be either trivial or elusive to achieve, depending on your goals.
A matte purple is simple to formulate by adding cobalt to a magnesium matte. An opaque, glossy purple can be done either with encapsulation stain or chrome/tin. Some excellent clear, celadon-like lavenders are possible thanks to neodymium oxide. Beautiful variegated purples appear in reduced copper glazes. But a dark, translucent, glossy purple seems rare among published or commercial glazes.
Introduction
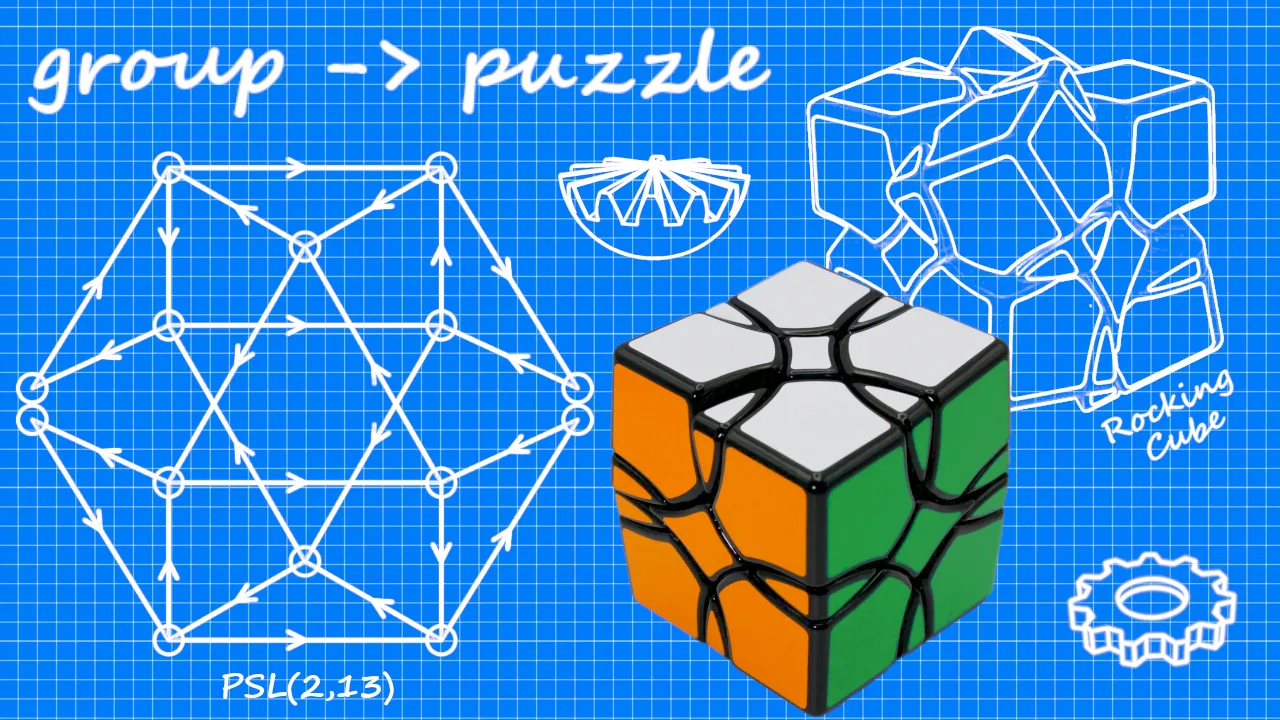
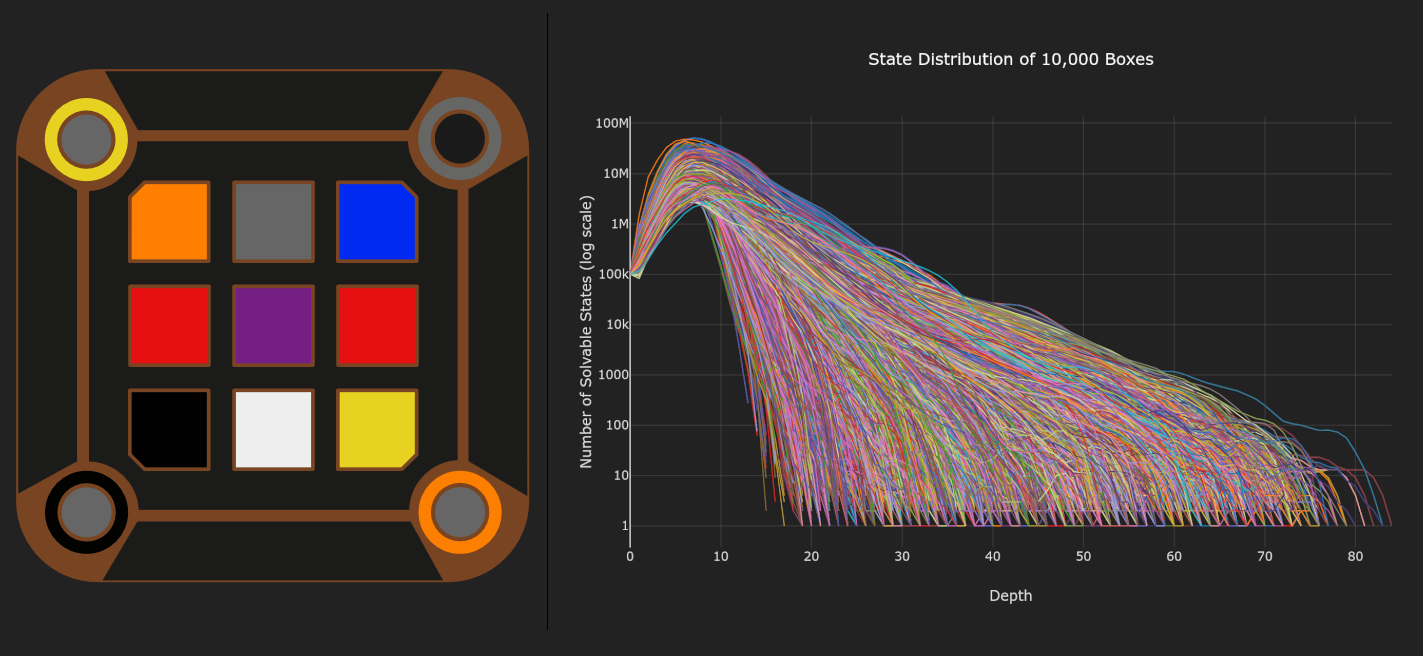
Mora Jai boxes are simple-looking puzzles that can be configured into a huge variety of challenges. The original set of puzzles from Blue Prince mostly have short, simple solutions (2-20 moves), but lengthy and difficult solutions can be constructed by exploring deeper state spaces of the tile grid.
Initially, I wanted to create a list of the most difficult configurations by cataloging the longest solutions, but it turns out that length is not the best predictor of difficulty. Many of the longest solutions rely on repetitive patterns rather than complex logic and novel mechanics.
Ultimately, the list of Challenge puzzles in my simulator was found using a combination of brute-force search, automated filtering, and manual inspection.
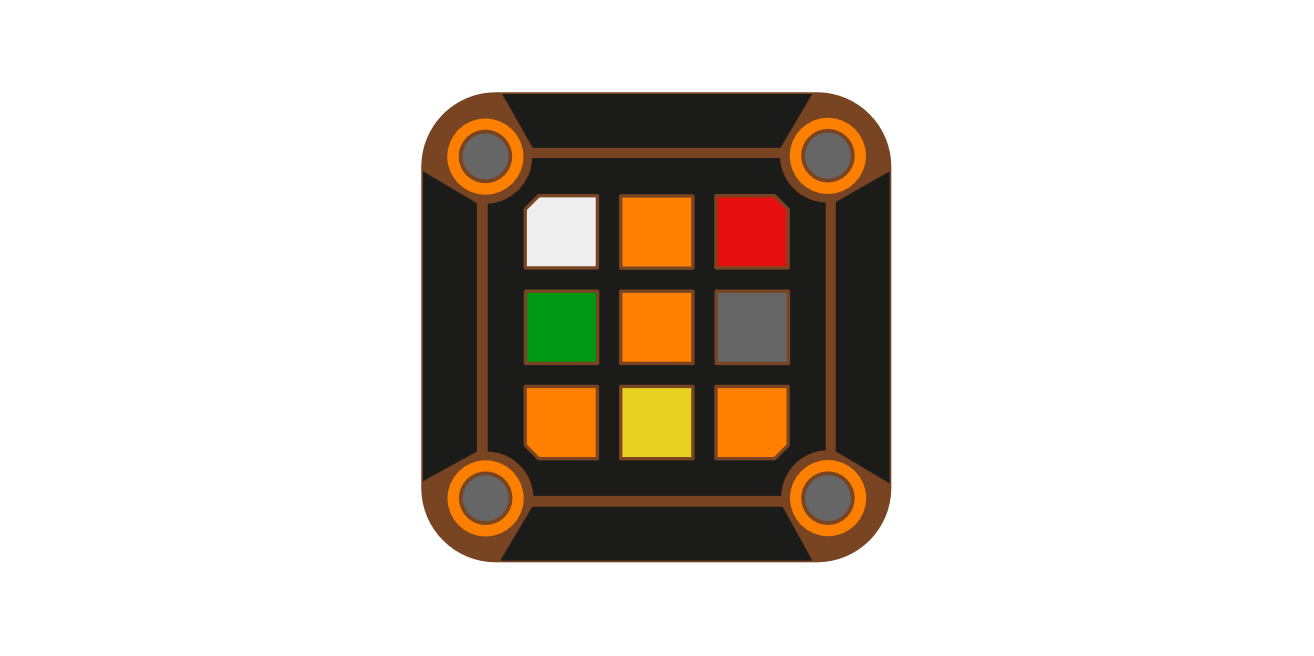

Mora Jai Box
A Mora Jai Box is a lock box that involves solving a 3x3 grid of colored tiles. Each color has a unique behavior (see rules). They are originally found in the puzzle/adventure game Blue Prince, but are interesting to analyze on their own.

Introduction
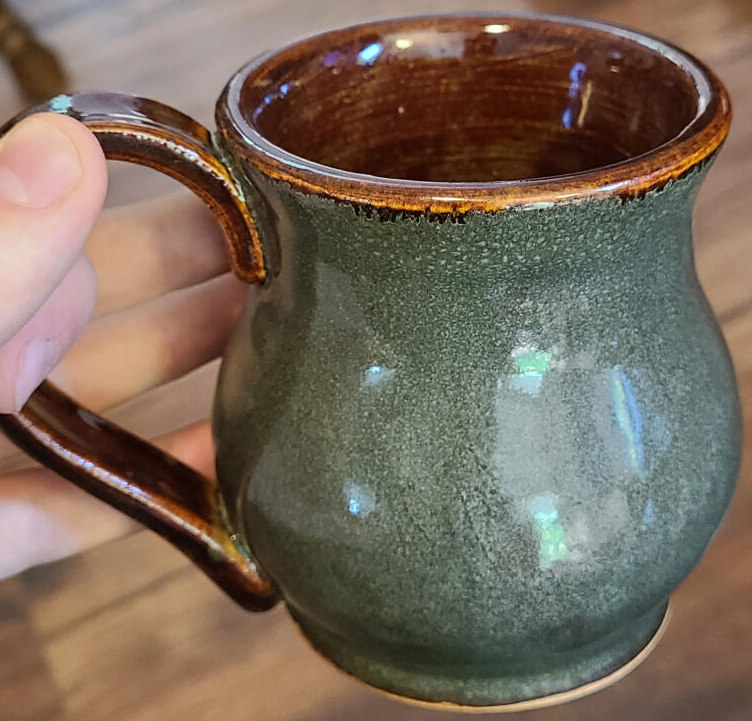
This page documents ongoing attempts to produce a rich, variegated green glaze using an iron/phosphorus mechanism in cone 6 borosilicate glaze.
Some key takeaways so far:
- A lithium-rich base produces a better green than a soda or potash base
- A small addition of lanthanum oxide appears to brighten the effect without changing the color
Iron/Phosphorus Glaze
Blue Hare, Hare’s Fur, or Floating Blue is a widely used effect in pottery studio glazes and commercial glazes.
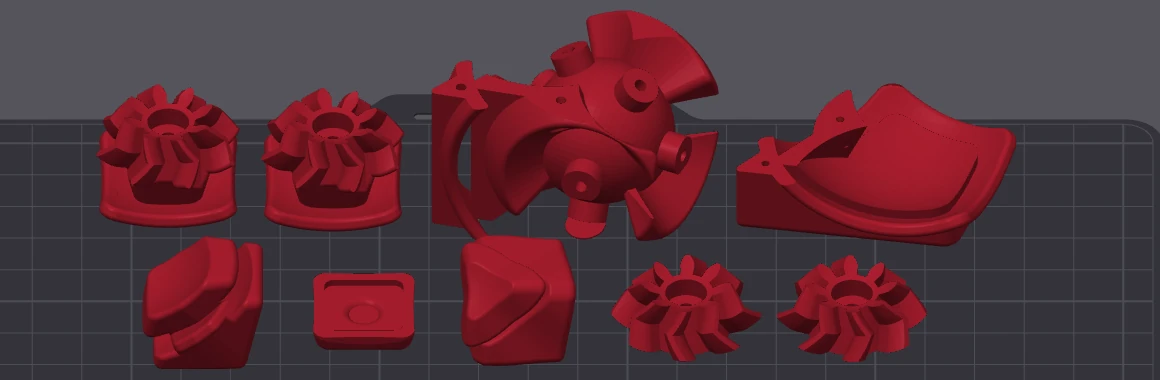
STL Files: https://quirkycubes.com/public/Illegal Slice Cube STL.zip
Sticker Template: https://quirkycubes.com/public/Illegal Slice Cube Stickers.zip
Hardware required:
- 4x M3 Springs (~10mm uncompressed)
- 4x M3 Washers
- 4x M3 x 8 Screws (socket or button head)
- 4x M3 x 16 Screws (socket or button head)
- 4x M2 x 8 Button Head Screws
- Lubricant
- Super glue (optional)
The Illegal Slice Cube is easy to print and doesn’t require any special hardware.
Bambu P1S print settings:
- 0.16 mm layers
- Support raft
- Half speed
- Auto snug supports at 25-30°
- Manual strong tree supports on core - just the overhangs
- 3 wall loops (for vapor smoothing)
- Polymaker ABS (Bambu brand ABS does not vapor-smooth)
- Bambu Support for ABS
Assembly
The core is made up of multiple parts that must be assembled in a specific order.
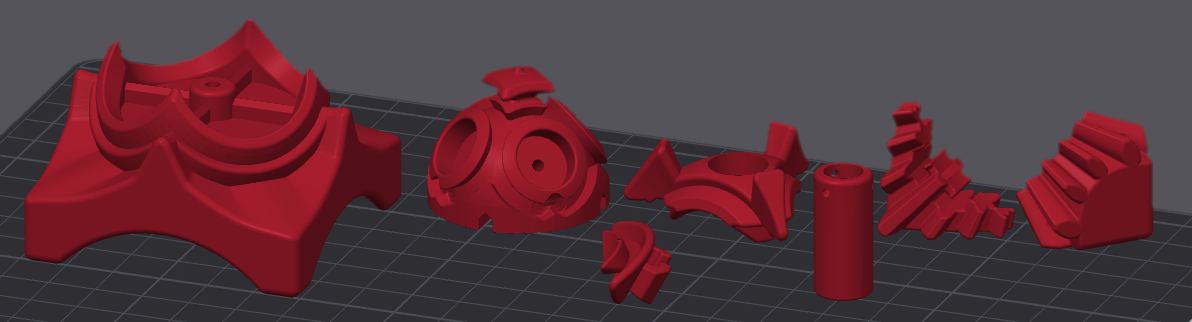
Updated 2025-03-16
STL Files (v2): https://quirkycubes.com/public/QuaternionCube_STL_v2.zip
Sticker Template (SVG, Silhouette Studio): https://quirkycubes.com/public/QuaternionCube_Stickers_v2.zip
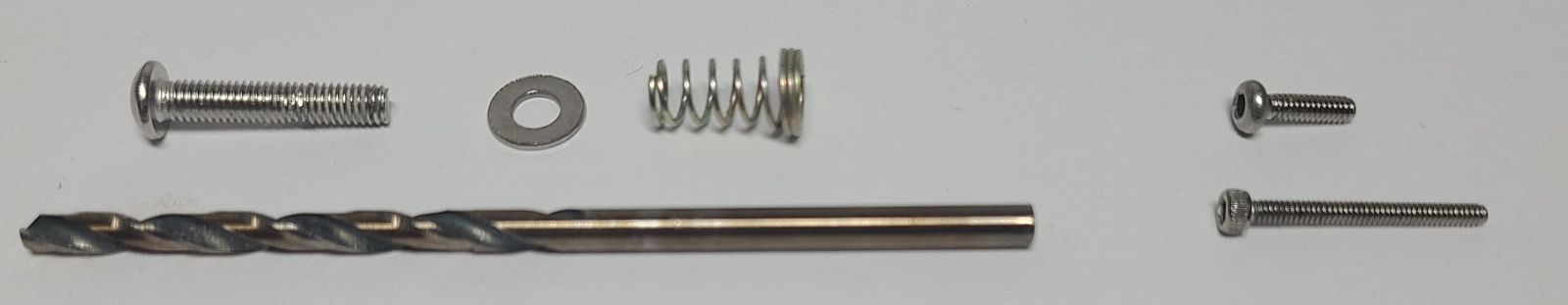
Hardware required:
- 5x M3 Springs (~10mm uncompressed)
- 5x M3 Washers (6.9mm dia)
- 5x M3 x 20mm Screws (button or socket)
- 12x M2 x 8 Button Head Screws
- 8x M1.6 x 16 Socket Head Screws
- 7/64" drill bit
I printed my copy out of ABS and vapor-smoothed it to post process it. I don’t see any reason that it wouldn’t work in PLA, but you will need to sand the edge hooks a little to get smooth motion. Here are the settings I use on a Bambu P1S:
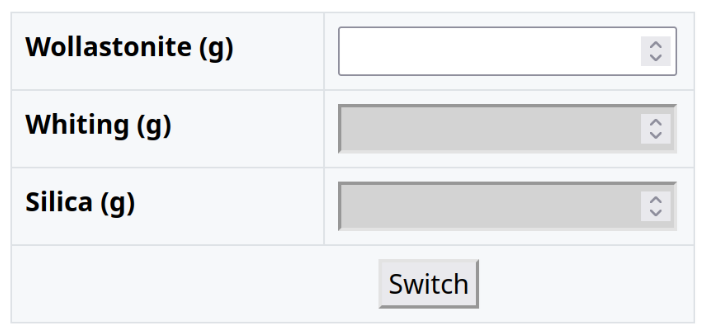
Glaze Material Substitutions
This page provides a set of calculators to help with calculating common material substitutions in glaze recipes.
Warning: These calculators are based on theoretical UMF analysis of the materials, and I have not verified them experimentally. Oxide analysis isn’t the only factor that determines how a material will behave in a glaze.
Each calculator allows for conversions between two material forms. Click “Switch” to toggle the conversion direction. Red cells indicate that a material should be subtracted from the recipe.
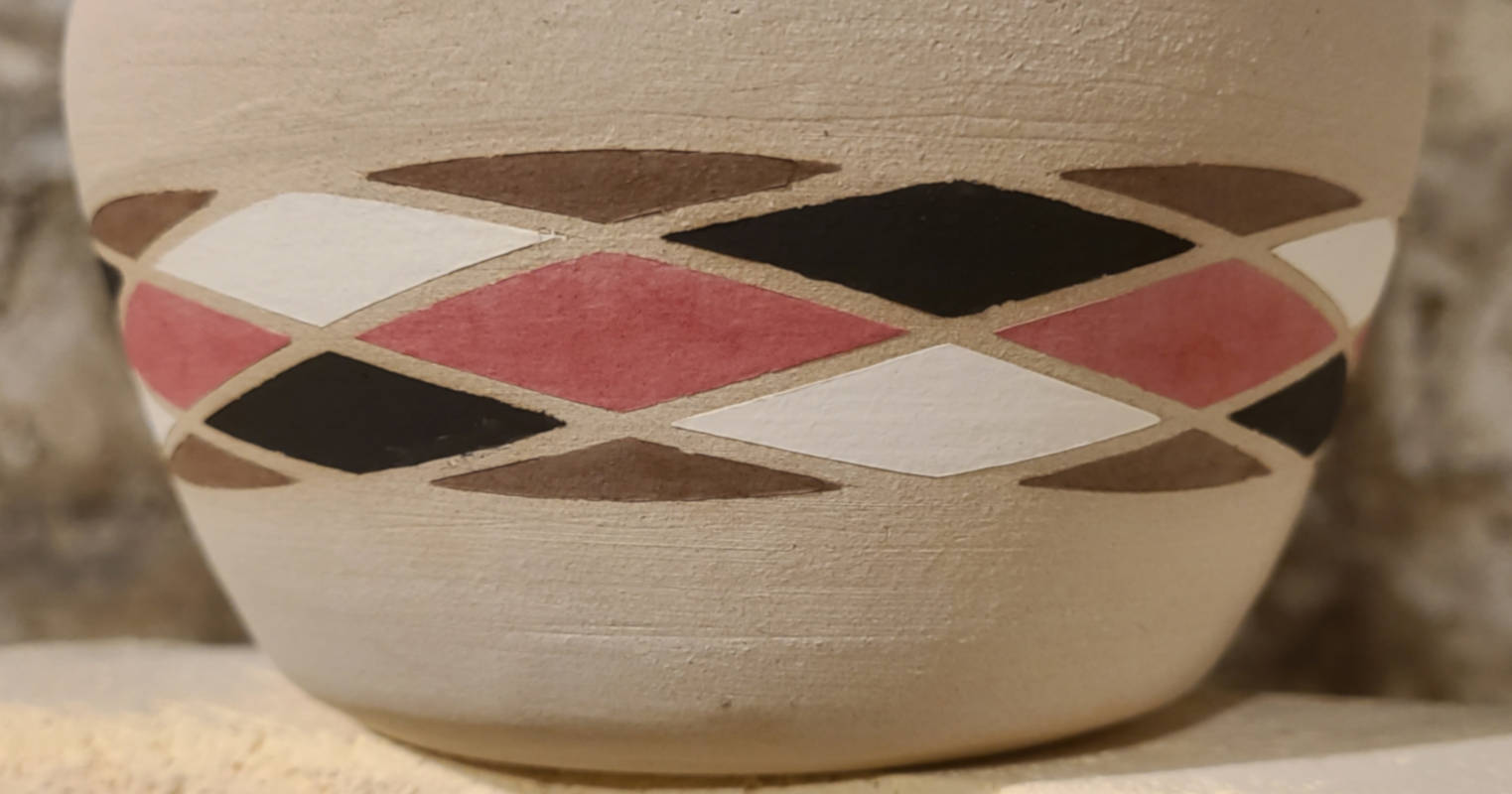

Wrapping vector artwork around a conical object in Inkscape
Free vector editing tools are pretty lacking in intuitive ways to wrap a template around a conical object (i.e. mug or vase). I aim to produce a vinyl decal that can be applied perfectly to a ceramic piece without any stretching.
This post is not a step-by-step procedure, but rather a general overview of the steps that I use to fit vector artwork to pieces of pottery using Inkscape and a vinyl cutter.
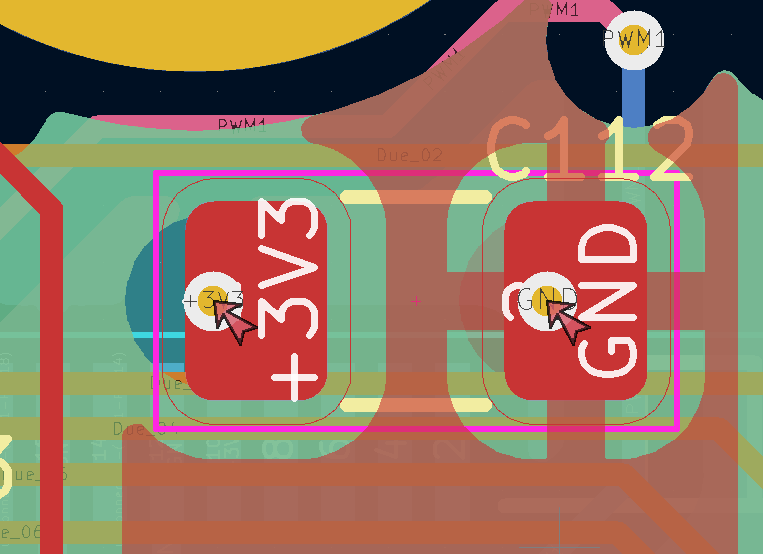
Current development builds for KiCAD 7 include the new constraint keyword physical_hole_clearance for detecting hole and pad collisions within a common net. This is useful for detecting via-in-pads which are often undesirable, as some PCB vendors upcharge to plug vias that could cause wicking during assembly.
To set up the custom design rule, first install a nightly build of KiCAD (6.99). Please note that saving a project with a development version of KiCAD will prevent older versions from opening the PCB file. To prevent this, I run the DRC from KiCAD 6.99 and make the necessary changes from KiCAD 6.